What, When, Where, How, Who?
Obscureness
Introduction, Important Definitions and Related Concepts:
Obscureness means absence or deficiency of light:
dark,
darkness,
dimness,
duskiness,
murkiness,
obscurity. See
light/darkness. Dark means Lacking or having very little light: a
dark corner. Darkness (also called lightlessness) is the
absence of light.
Dimness means lacking in brightness: a dim room.
Dusky is Characterized by little or inadequate light; shadowy. Murky
means Dark, dim, or gloomy: a murky dungeon.
See Synonyms at dark.
Obscure means shrouded in
or hidden by darkness. Light, or visible light, is
electromagnetic radiation of a
wavelength
that is visible to the human
eye (about 400–700
nm).
Dim is a low level of
illumination (lighting); lacking in brightness.
A room, in
architecture, is any distinguishable space within a structure.
A dungeon is a place where prisoners are kept.
Electromagnetism is the
physics of
the electromagnetic field: a
field which exerts a
force on
particles that possess the property of
electric charge, and is in turn affected by the presence and motion of those
particles. Radiation, as used in
physics, is
energy in the
form of
waves
or moving
subatomic particles. In
physics,
wavelength is the distance between repeating units of a propagating
wave of a given
frequency.
Eyes are
organs that detect
light. Nanometre,
an SI unit of length, equal to
10sup>-9 m
(a thousand-millionth of a metre). Lighting includes both artificial
light sources such as lamps and natural illumination of interiors from
daylight.
Architecture is the
art and
science of
designing
buildings and other physical
structures. Physics is the
science of
matter[1]
and its
motion,[2][3]
as well as space
and time[4][5]
— the science
that deals with concepts such as
force,
energy,
mass, and
charge. In
abstract algebra, a field is an
algebraic structure in which the operations of addition, subtraction,
multiplication and
division (except division by zero) may be performed, and the same rules hold
which are familiar from the
arithmetic
of ordinary numbers.
In physics,
force is what causes a
mass to
accelerate. Particle is a very small piece or part; a tiny portion or speck.
Electricity (from
New Latin
ēlectricus, "amber-like")
is a general term that encompasses a variety of phenomena resulting from the
presence and flow of
electric charge. Electric charge is a fundamental conserved property
of some
subatomic particles, which determines their
electromagnetic interaction. In
physics and
other sciences,
energy (from the
Greek ενεργός, energos, "active, working")[1]
is a
scalar
physical quantity that is a property of objects and systems which is
conserved by nature. A wave is a disturbance that propagates through
space and
time, usually with
transferrance of
energy. A subatomic particle is an
elementary or
composite
particle smaller than an
atom. Frequency
is a
measure of the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit
time. In
biology, an
organ (Latin:
organum, "instrument, tool", from
Greek όργανον - organon, "organ, instrument, tool") is a group of
tissues that perform a specific function or group of functions. 10 (ten)
is an even
natural number following
9
and preceding
11.
Supremum,
in mathematics, the least upper bound of a partially ordered set. 9 (nine)
is the
natural number following
8
and preceding
10.
Source means the place where something begins, where it springs into being; "the
Italian beginning of the Renaissance" "Jupiter was the origin of the radiation";
"Pittsburgh is the source of the Ohio River";
"communism's Russian root" [syn:
beginning, origin,
root,
rootage]. Daylight means the
light of day; sunlight. Art refers to a diverse range of human activities
and artifacts, and may be used to cover all or any of
the arts,
including music,
literature
and other forms. Science (from the Latin scientia, 'knowledge'),
in the broadest sense, refers to any
systematic
knowledge or
practice. Design, usually considered in the context of
applied
arts,
engineering,
architecture, and other
creative
endeavors, is used both as a
noun and a
verb. In
architecture,
construction,
engineering and
real estate development the word building may refer to one of the
following: Any man-made structure used or intended for supporting or sheltering
any use or continuous
occupancy,
or An act of
construction. Structure is a fundamental and sometimes intangible
notion covering the recognition, observation, nature, and stability of patterns
and relationships of entities. In science, matter is commonly defined as
the substance
of which physical objects are composed, not counting the contribution of various
energy or
force-fields, which are not usually considered to be matter per se (though
they may contribute to the
mass of objects).
Motion (physics), any physical movement or change in position or place.
Science considers space to be a
fundamental quantity (a quantity which can not be defined via other
quantities because other quantities — like
force and
energy — are
already defined via space). Time is a nonspatial continuum in which events occur
in apparently irreversible succession from the past through the present to the
future. Mass is a fundamental concept in
physics,
roughly corresponding to the intuitive idea of "how much matter there is in an
object". One well-known proposal is that an object is abstract if and only if it
lacks a location in space. Algebra is a branch of
mathematics concerning the study of
structure,
relation and
quantity.
Specifically, if c times b equals a, written:
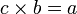 where b is not
zero,
then a divided by b equals c, written:
where b is not
zero,
then a divided by b equals c, written:
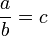 .
Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the
Greek word αριθμός = number) is the oldest and most elementary branch
of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple
day-to-day counting to advanced
science and
business
calculations. A number is an abstract idea used in
counting
and
measuring. In
physics, acceleration is said as the
rate of
change of
velocity, or as the second
derivative
of position (with respect to time). Latin (lingua latīna,
pronounced
[laˈtiːna]) is an ancient
Indo-European language that was spoken in the
Roman Republic and the
Roman
Empire. Amber is the name for
fossil
resin or tree sap
that is appreciated for its colour. As a preposition or adjective, it comes from
the
Middle English like meaning "similar",
which in turn comes from
Anglo-Saxon gelīc and
Old Norse
líkr. Interaction is a kind of
action that occurs as two or more objects have an
effect upon one
another. Greek (ελληνική γλώσσα
IPA:
[eliniˈkʲi ˈɣlosa] or
simply ελληνικά
IPA:
[eliniˈka] — "Hellenic")
has a documented history of 3,400 years, the longest of any single
natural language in the
Indo-European
language family. A scalar is a variable that only has
magnitude,
e.g. a speed of
40 km/h. Physical means the nature (physicality)
of a
physical entity. Quantity is a kind of which exists as magnitude or
multitude. In
particle physics, an
elementary particle is a particle of which other, larger particles are
composed. Composite means made up of distinct components; compound. An atom
is the smallest particle characterizing a
chemical element.
Measure (mathematics), a way to assign non-negative real numbers to subsets.
Biology (from Greek: βίος, bio, "life";
and λόγος, logos,
"speech" lit. "to talk about life"), also referred to as the biological
sciences, is the
scientific study of
life. Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected
cells that perform a similar function within an organism.
even and odd numbers -- even if divisible by 2. Natural means Present in or
produced by nature: a natural pearl. 11
(eleven) is the
natural number following
10
and preceding
12.
8 (eight) is the
natural number following
7
and preceding
9.
Beginning means The act or process of bringing or being brought into being; a
start.
Origin (start), the beginning, starting-point, cause, or ultimate source,
from which a thing is derived. It is better to define root as a part of a
plant body that bears no leaves, and therefore also lacks
nodes. Rootage means establishment by or as if by roots. An often-cited
definition of music, coined by
Edgard Varèse, is that it is "organized sound" (Goldman 1961, 133).
Literature is a body of (usually) written works related by subject-matter,
by language or place of origin, or by dominant cultural standards.[1]
Knowledge is defined (Oxford
English Dictionary) variously as (i) expertise, and skills acquired by a
person through
experience
or education;
the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject, (ii) what is known in a
particular field or in total; facts and information or (iii) awareness or
familiarity gained by experience of a fact or situation. Systematic means
presented or formulated as
a coherent body of ideas or principles <systematic
thought>.
Practice (learning method), a method of learning by repetition. Applied
means to
.
Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the
Greek word αριθμός = number) is the oldest and most elementary branch
of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple
day-to-day counting to advanced
science and
business
calculations. A number is an abstract idea used in
counting
and
measuring. In
physics, acceleration is said as the
rate of
change of
velocity, or as the second
derivative
of position (with respect to time). Latin (lingua latīna,
pronounced
[laˈtiːna]) is an ancient
Indo-European language that was spoken in the
Roman Republic and the
Roman
Empire. Amber is the name for
fossil
resin or tree sap
that is appreciated for its colour. As a preposition or adjective, it comes from
the
Middle English like meaning "similar",
which in turn comes from
Anglo-Saxon gelīc and
Old Norse
líkr. Interaction is a kind of
action that occurs as two or more objects have an
effect upon one
another. Greek (ελληνική γλώσσα
IPA:
[eliniˈkʲi ˈɣlosa] or
simply ελληνικά
IPA:
[eliniˈka] — "Hellenic")
has a documented history of 3,400 years, the longest of any single
natural language in the
Indo-European
language family. A scalar is a variable that only has
magnitude,
e.g. a speed of
40 km/h. Physical means the nature (physicality)
of a
physical entity. Quantity is a kind of which exists as magnitude or
multitude. In
particle physics, an
elementary particle is a particle of which other, larger particles are
composed. Composite means made up of distinct components; compound. An atom
is the smallest particle characterizing a
chemical element.
Measure (mathematics), a way to assign non-negative real numbers to subsets.
Biology (from Greek: βίος, bio, "life";
and λόγος, logos,
"speech" lit. "to talk about life"), also referred to as the biological
sciences, is the
scientific study of
life. Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected
cells that perform a similar function within an organism.
even and odd numbers -- even if divisible by 2. Natural means Present in or
produced by nature: a natural pearl. 11
(eleven) is the
natural number following
10
and preceding
12.
8 (eight) is the
natural number following
7
and preceding
9.
Beginning means The act or process of bringing or being brought into being; a
start.
Origin (start), the beginning, starting-point, cause, or ultimate source,
from which a thing is derived. It is better to define root as a part of a
plant body that bears no leaves, and therefore also lacks
nodes. Rootage means establishment by or as if by roots. An often-cited
definition of music, coined by
Edgard Varèse, is that it is "organized sound" (Goldman 1961, 133).
Literature is a body of (usually) written works related by subject-matter,
by language or place of origin, or by dominant cultural standards.[1]
Knowledge is defined (Oxford
English Dictionary) variously as (i) expertise, and skills acquired by a
person through
experience
or education;
the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject, (ii) what is known in a
particular field or in total; facts and information or (iii) awareness or
familiarity gained by experience of a fact or situation. Systematic means
presented or formulated as
a coherent body of ideas or principles <systematic
thought>.
Practice (learning method), a method of learning by repetition. Applied
means to
Next
